ANSYS Zemax OpticStudio & OpticBuilder 2023 R1.00 Win x64
"softddl.org"
11-01-2023, 22:29
-
Share on social networks:
-
Download for free: ANSYS Zemax
-

ANSYS Zemax OpticStudio & OpticBuilder 2023 R1.00 | 6.4 Gb
Product:ANSYS Zemax OpticStudio & OpticsBuilder *
Version:2023 R1.00
Supported Architectures:x64
Website Home Page :www.ansys.com
Languages Supported:english
System Requirements:Windows **
Size:6.4 Gb
Zemax, part Ansys, is pleased to announce the availability of OpticStudio & OpticsBuilder 2023 R1.00 is the standard for optical, illumination, and laser system design in universities around the world, and in leading companies throughout the optics industry.

ANSYS Zemax OpticStudio & OpticBuilder 2023 R1.00 | 6.4 Gb
Product:ANSYS Zemax OpticStudio & OpticsBuilder *
Version:2023 R1.00
Supported Architectures:x64
Website Home Page :www.ansys.com
Languages Supported:english
System Requirements:Windows **
Size:6.4 Gb
Zemax, part Ansys, is pleased to announce the availability of OpticStudio & OpticsBuilder 2023 R1.00 is the standard for optical, illumination, and laser system design in universities around the world, and in leading companies throughout the optics industry.
Ansys Zemax OpticStudio 2023 R1.00 - Date: January 12th, 2023
LUMERICAL SUB-WAVELENGTH DYNAMIC LINK DLL (PREMIUM AND ENTERPRISE EDITIONS)
Enhanced support for 2D gratings with the Lumerical Sub-wavelength Dynamic Link DLL.
This new Diffraction DLL enables simulation of 2D gratings by dynamically linking to Ansys Lumerical FDTD. When rays hit a grating in Ansys Zemax OpticStudio, the diffraction efficiency is calculated using the Lumerical RCWA solver.
To run this DLL, the Lumerical FDTD needs to be installed on the same PC, so that this DLL can call Lumerical for calculation.
LUMERICAL SUB-WAVELENGTH DLL (ALL EDITIONS)
Accurately simulate a grating by importing Lumerical data from a static file.
This DLL allows users to simulate a grating by loading pre-calculated diffraction efficiency data saved in a JSON file. The contents of this file can be calculated by and exported from Ansys Lumerical FDTD (calculations use the Lumerical RCWA solver). Users can find more details about how to export this JSON file here: Speos Lumerical Sub-wavelength Model. Users can also find more information about importing the JSON file into OpticStudio using this DLL, search "How to load grating data from Lumerical into OpticStudio" here: Knowledgebase (zemax.com).
COMPOSITE SURFACE (ALL EDITIONS)
Tolerance surface irregularities for any physical surface.
The new Composite Surface capability enables you to easily create complex surface geometries in sequential mode by allowing the sag of any surface to be added to the sag of a base surface, for any surface types where real sag is used to characterize the behavior of the optical component. Any number of Composite Surfaces can be stacked together, and all the sags will be summed to the base surface.
This advanced functionality enables several new capabilities in OpticStudio, including the ability to directly tolerance the surface irregularity of any sag-based surface - with no workaround needed! Direct surface irregularity tolerancing has been enabled for all sag-based surfaces in the sequential mode of OpticStudio using the TEZI operand.
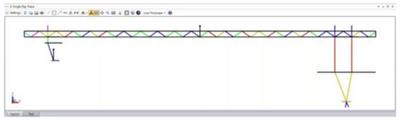
NON-SEQUENTIAL SINGLE RAY TRACE (ALL EDITIONS)
Enables analysis and visualization to study ray propagation in an NSC optical system.
The new Single Ray Trace enables you to trace a single ray in non-sequential mode without affecting your original system. The NSC Single Ray Trace enables analysis and visualization on a ray-by-ray basis to study the ray propagation in a non-sequential optical system. This is important for understanding the behavior of complex imaging systems being modeled in non-sequential mode, such as exit pupil expanders used in AR systems.
NSC GEOMETRIC MTF (ALL EDITIONS)
Calculate Geometric MTF on a detector in non-sequential mode.
This new feature allows users to calculate the Geometric MTF from the irradiance distribution on a detector in non-sequential mode. This feature replaces the Geometric MTF option in the Detector Viewer.
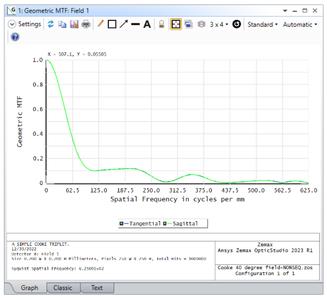
The Geometric MTF is calculated using all rays coming from all sources that land on the detector, not just rays originating from a single source in the system. Therefore, the results may differ between sequential and non-sequential calculations of the Geometric MTF. The results may also differ if the non-sequential system includes mechanical components with which rays may interact or if the system is set for rays to be split or scattered.
Importantly, the Geometric MTF in non-sequential mode is calculated in cycles/millimeters, regardless of the chosen MTF Units in the System Explorer.
NSC SURFACE SAG (ALL EDITIONS)
Easily analyze the shape of any complex surface in non-sequential mode to ensure manufacturability.
This new built-in analysis in OpticStudio uses non-sequential ray tracing to calculate the sag values of a specified face of an object defined in the Non-sequential Component Editor (NSCE).
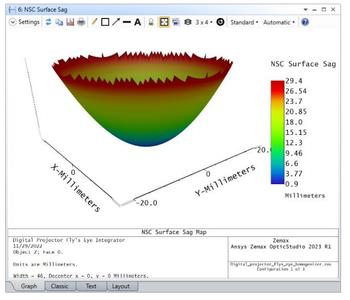
The rays used for the sag calculation can be visualized in the Layout tab, which greatly assists with troubleshooting setup of the analysis.
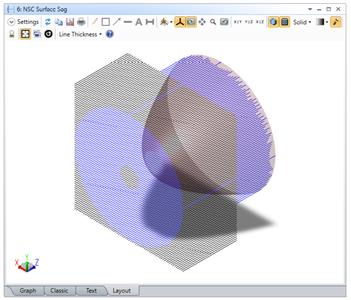
The settings for this analysis include a "Keep Object Tilts" checkbox, which enables preservation of the object's original x and y tilt. If this box is checked, the analysis will account for the tilts of the object when calculating the sag, and they'll be ignored if this box is unchecked.The analysis also lets the user remove the base radius, best-fit sphere, base sag, average sag, or minimum sag. The average and minimum sag allow for piston removal or to anchor the sag map to the lowest sag value.
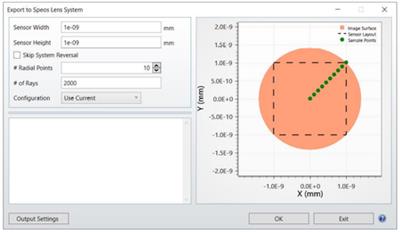
UPDATES TO EXPORT SPEOS LENS SYSTEM (ALL EDITIONS)
Added features include skip system reversal, configuration options, and sensor map visualization.
New features include the ability to skip the automated reversal step during the computation of systems that are reversed manually and the ability to export a specific configuration from a multiconfiguration system. The ability to save specific parameters in the Speos Exporter Output Settings has also been included in the User Interface. The parameters that can be saved include distortion, variable entrance pupil position, sharpness losses, depth of field and resolution.
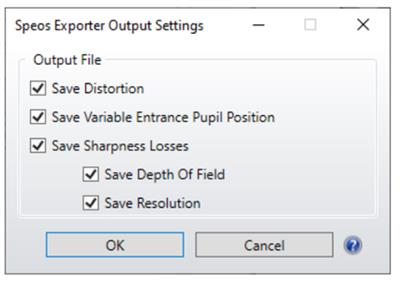
A new sensor layout has been added for an improved visual representation of the image plane sampling. Output distortion file settings are featured to customize the output data by including or excluding specific input parameters.
PREPARE FOR OPTICSBUILDER: HARD APERTURE (ALL EDITIONS)
Improvements to NSC Hard Aperture for Stop surfaces.
A new feature has been added to improve the conversion of Stop surfaces to NSC Apertures during the creation of ZBD files. This feature allows users to determine whether the Stop surface is converted to either an annulus ring (for circular apertures) or a rectangular aperture in non-sequential mode when the Stop is not located on an optical component (i.e., is not the surface of a lens or a mirror). The new mechanical Stop-half-width input enables the user to define the external diameter/width of the non-sequential objects.
The addition of the Status tab in Prepare for OpticsBuilder shows a log of events to help with error handling when preparing the ZBD files.
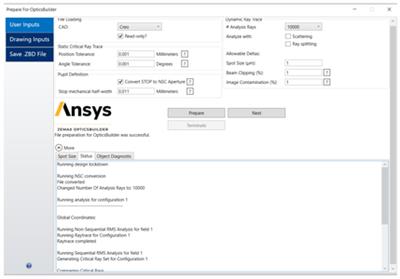
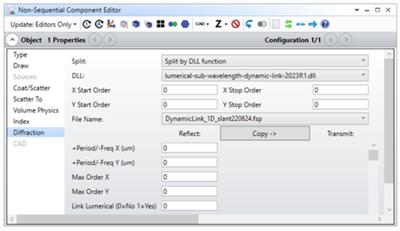
NSC DIFFRACTION PROPERTIES (ALL EDITIONS)
Enhanced User Interface for 2-d dimensional diffraction orders.
The user interface of the Diffraction tab within the Properties dialog of the Non-Sequential Component Editor has been updated to allow for separate specification of the start and stop orders in X and Y. This is necessary for accurate characterization of 2D gratings.
A new Copy button has also been added to the user interface that carries out a one-time copy from the Reflect to the Transmit settings for the grating. This allows users to define parameters for both Reflect and Transmit when setting up grating parameters.
The new user interface allows users to customize their diffraction DLLs to better match their requirements. Users can check the built-in Diff2DSample.dll and its source code Diff2DSample.cpp to learn more about how to build a DLL with this new user interface.
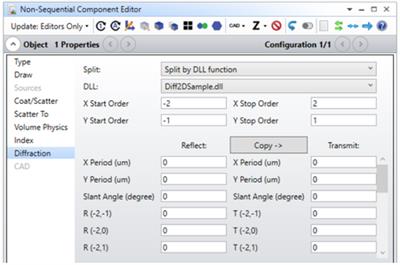
STAR: ACTIVE RIGID BODY MOTIONS (RBMS) (ENTERPRISE EDITION)
New capability for Rigid Body Motions (RBMs).
The Structural, Thermal, Analysis and Results (STAR) functionality in the Enterprise edition of Ansys Zemax OpticStudio now features a new capability to decouple rigid-body motions (RBMs) from higher-order surface deformations in the structural datasets that are loaded from any finite element analysis platform. New checkboxes have been added to the Structural Data Summary that enable you to turn on or off the contributions of Fitted Deformations (excluding RBMs) or Extracted RBMs for each surface. These features enable or disable the contributions without needing to modify the FEA datasets directly.
Also, a new Structural Options drop-down menu is available to enable and disable the Fitted Deformations and Extracted RBMs for all surfaces with one click.
UDA ON NSQ EXTENDED POLYNOMIAL LENS (ALL EDITIONS)
Additional support for User Defined Aperture (UDA).
A User Defined Aperture (UDA) will now be added on top of the Extended Polynomial Lens object in non-sequential mode when creating this object during conversion of an Extended Polynomial sequential surface mirror with a user-defined aperture on it. This is important for modeling complex geometries supported by the Extended Polynomial surface and lens, which often require specific apertures to deal with effects at the surface boundaries.
EXPORT TO PANDAO (ALL EDITIONS)
Determine the optimal fabrication chain at any point during the optical design process.
PanDao (
https://pandao.ch/The Export to PanDao tool is a ZOS-API standalone application that helps automate the process by extracting the relevant data from an OpticStudio lens file and writing this to a JSON file that can subsequently be read in by the PanDao toolset.
This tool currently supports on-axis systems that use Standard surfaces that are spherical (the conic constant must be zero), Even Asphere, Extended Asphere, and Extended Odd Asphere surface types. Both refractive and reflective surfaces are supported.
LICENSE BORROWING (ALL EDITIONS)
Continue to work offline when being unable to contact the license server.
A new Ansys Client Settings utility has been added to enable borrowing an Ansys Zemax license that can be used without your computer making contact with the license server. This is helpful in cases where the client workstation won't be able to directly communicate with the license server for a while, such as a laptop going to a remote worksite or someone working temporarily from home without a VPN. See the built-in help file for details.
MORE FILE TYPES SUPPORTED BY PROJECT DIRECTORIES (ALL EDITIONS)
The Project Directory now supports even more of your files.
Introduced in Zemax OpticStudio 21.3, The Project Directory system enables easy packaging and storage of important Zemax files so that they can be easily accessed a manipulated on a project-byproject basis. A Project Directory can be created from an existing OpticStudio design by using the Convert to Project Directory button in the File tab.
With Ansys Zemax OpticStudio 2023 R1, Project Directories now also support the following file types:
- Physical Optics Propagation (POP) files (.ZBF, .ZMM)
- Objects/Sources/IESNA files (.IES, .DAT)
- Configuration files (.CFG)
- Objects/Sources/Source Files (.CRS, .FFD, .RRD, .DAT, .SDF)
....................and more
Ansys Zemax OpticsBuilder 2023 R1.00 - Date: January 12th, 2023
FOLD MIRROR TOOL FIXES
Fold your system to fit within tight, space-constrained assemblies.
A legacy tool in need of maintenance, the Fold Mirror Tool offers users a way to simulate their environment and place fold mirrors that allow their optical product to fit in tight space-constraints. An overhaul of the tool addressed all known errors to make it less buggy for users. This important update also positions the Fold Mirror Tool for greater additional functionality in the future.
Fold Mirror Tool fixes include:
- Fold mirror uses "MIRROR" material instead of taking on optical properties from nearby components.
- Error messaging relating to the Fold Mirror Tool has been streamlined.
- Ensuring ray footprint boundaries are applied on all components when a fold mirror is present,and the Ray Footprint Boundaries tool has been chosen.
- Giving a correct preview that matches the applied final component placement when a mechanical sub-assembly is present.
- Setting a correct default fold mirror size (radius) to equal the referenced maximum clear aperture divided by the cosign of the tilting angle.
- Any crashes no longer occur when making changes to the fold mirror tool settings.
- Mechanical components are correctly assigned in the Optics Manager whereas previously they would sometimes be mistaken for optical components and moved to the wrong section of the Optics Manager.
- Ensuring that the Simulation feature will ray trace through a system that contains both a mirror from OpticStudio and a new fold mirror placed using the tool in OpticsBuilder.
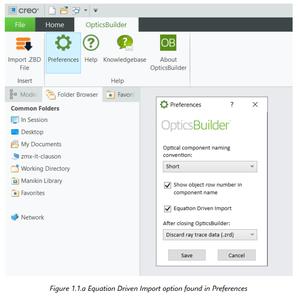
EQUATION-DRIVEN IMPORT OPTION
Equation-driven import now allows you to expose the equations that create the lens surface.
OpticsBuilder imports lens geometries using their surface equation in the background and creates the parts using splines creating parametric part files. This new equation-driven import functionality will allow users to generate surfaces using these equations while exposing and tying the equation to the part file. This allows users to store their optical parts in a PDM and recall the equations used to create the part. The equation-driven surfaces now have more data and allow users to manipulate the surfaces, such as creating lens edges, with more ease. The equation driven import option is now available for standard, even asphere, odd asphere, binary 2, binary 2a and off-axis mirror nonsequential component types.
ANSYS ZEMAX TROUBLESHOOTER
Updated Ansys Zemax Troubleshooter
In OpticsBuilder 2022 R2.02 we introduce an updated Ansys Zemax Troubleshooter that now allows an open text field for users to enter an explanation of their issue. This newly updated Troubleshooter tool also connects to the Ansys licensing to verify and eliminate any licensing issues which will speed up time to resolution.
BUG FIXES
OpticsBuilder 2023 R1 includes the following bug fixes:
- Off-Axis Mirror - The lens geometry did not change when the radius of the off-axis mirror was modified from 0 to another value through the Edit Optical Properties window.
- Detector Preview - The preview function was not showing the correct detector type after was changed in the Edit Optical Properties window.
- Optomechanical component appearance - If a user makes changes to an optical component using the CAD tools, it changes designation from optical to optomechanical. If the user then exported the .ZBD file and re-imported the .ZBD file, the appearance of this part was changed.
- Simulation precision - When changing the precision settings for a Simulation, the image on the detector was not updated.
- Boundary Rays - The Boundary Rays were hidden after closing and adding a new .ZBD file into Creo without using the Creo function "Erase Not Displayed" to clear the local workspace.
- Import stops occasionally - We have fixed an issue where, on occasion, OpticsBuilder would stop importing and would show a red "x". The user would have to restart Creo to allow OpticsBuilder to import.
- Simulation Results not updating - Some users were experiencing a scenario where they would make modifications to the mechanical annulus, run a Simulation, and not see updated Results that accurately reflected the modifications. The Simulation tool now updates and displays correct results every time.
- Schmidt-Cassegrain sample issues - Our Schmidt-Cassegrain sample file was having an issue where the material would change upon .ZBD export from OpticsBuilder. It also caused random crashes when importing the sample file into OpticsBuilder. Both issues are now resolved, and the sample file has been updated.
- Optics Manager and Ribbon disabled - If a user removed an inserted optical assembly, the Optics Manager was disappearing, and the top Ribbon menu was grayed out. We have ensured that the Optics Manager remains and only the optics are deleted when removing an optical assembly. We have also ensured that the top Ribbon menu remains active.
- Creo stalls without OpticsBuilder license activated - If a user had installed OpticsBuilder but didn't have an active OpticsBuilder license, clicking on "About OpticsBuilder" would cause Creo to stall. This issue is now resolved.
- Generate Report window - When opening the Generate Report window, it would hide in the background. The Generate Report window now stays open in the foreground.
- Update OpticsBuilder - In About OpticsBuilder, if a user clicked on "Check for Updates" an error message appeared. The "Check for Updates" button is now functioning correctly.
ANNOUNCEMENTS
ISX scattering will be deprecated after 2023 R1 release
The ISX scatter libraries will be removed from OpticsBuilder following the 2023 R1 release, as these libraries rely on obsolete Microsoft components that could potentially introduce IT or security vulnerabilities in the future. New BSDF scatter libraries will be made available in OpticsBuilder in a future release, based on a format that can be easily updated and maintained in a secure manner
Ansys Zemax OpticStudio'sintuitive user interface includes easy-to-learn tools and wizards, which enable efficient simulation and design of any optical system. With more than 200 field points you can set up even the most complex freeform and non-rotationally symmetric systems. OpticStudio also includes a suite of optical engineering tools to analyze the performance of your system. In addition to the classic analysis functions, Zemax OpticStudio also offers Full-field Aberration analysis to improve freeform designs; contrast analysis for MTF optimization; and Image Simulation to produce photorealistic images of object scenes.
Zemax OpticStudio - Everything you need to design optical systems
To turn optical designs into reality, teams of engineers need to coordinate around one common goal. Now CAD users don't have to recreate optical designs into CAD formats. WithOpticsBuilder, CAD users can directly convert complete optical designs from OpticStudio into CAD, analyze how packaging impacts performance, and export optical drawings to manufacturing-saving costs and expensive prototypes.
OpticsBuilder Insights: Using the OpticsBuilder's Export .ZBD file feature
Ansysis the global leader in engineering simulation. Through our strategy of Pervasive Engineering Simulation, we help the world's most innovative companies deliver radically better products to their customers. By offering the best and broadest portfolio of engineering simulation software, we help them solve the most complex design challenges and create products limited only by imagination. Founded in 1970, Ansys is headquartered south of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S.A. Visitwww.ansys.comfor more information.
In 2021,Ansys acquired Zemax, the world's number one optical simulation toolset and Zemax is now "An Ansys Company." that is transitioning into the Ansys family. Initial connections between OpticStudio and Ansys Mechanical are already in place, and you will see further integration until it becomes part of the Ansys multiphysics capability.

Buy Premium From My Links To Get Resumable Support,Max Speed & Support Me
1DL
n5uuy.SET.UP.part1.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part2.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part3.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part4.rar
 ]DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET [/url]
]DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET [/url]
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
 ]DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM [/url]
]DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM [/url]
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM

DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
n5uuy.SET.UP.part1.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part2.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part3.rar
n5uuy.SET.UP.part4.rar
 ]DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET [/url]
]DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET [/url]DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
DOWNLOAD FROM RAPIDGATOR.NET
 ]DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM [/url]
]DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM [/url]DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM UPLOADGIG.COM

DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
DOWNLOAD FROM NITROFLARE.COM
Links are Interchangeable - No Password - Single Extraction
The minimum comment length is 50 characters. comments are moderated




